Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: Diagnosis & Management (Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Candida albicans), Trichomoniasis, Chlamydial Cervicitis, Gonorrheal Cervicitis)
Management Sheet Cause Key Features First-Line Treatment Alternative / Notes Partner Treatment Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) Thin gray-white discharge, fishy odor, pH >4.5, clue cells ✅ Metronidazole 500 mg PO bid × 7 days Clindamycin 300 mg PO bid × 7 days ❌ Not required Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Candida albicans) Thick white “cottage cheese” discharge, itching, pH ≤4.5 ✅ Fluconazole 150 mg PO single dose Topical azole (Clotrimazole 500 mg PV single dose) ❌ Not required Trichomon

Glenn then Fontan Circulation Simplified: Understanding Single-Ventricle Palliation
🫀 1. The “Single-Ventricle” Problem Some babies are born with only one functional ventricle (either LV or RV can’t support circulation).Examples: Tricuspid atresia Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) Double-inlet ventricle Pulmonary atresia with intact septum Because of this, the heart cannot pump blood separately to lungs and body like a normal two-ventricle system. So we create a Fontan circulation , where systemic venous blood flows passively to the lungs (no ventric

Management of Rhinosinusitis (Sinusitis): Stepwise Approach from First Stage to Antibiotic Therapy
1. Definition and Classification Rhinosinusitis refers to inflammation of the mucosa of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.It often begins as viral rhinosinusitis and may progress to bacterial sinusitis in a small percentage of cases. Type Duration Typical Cause Acute ≤ 4 weeks Usually viral; bacterial if severe/persistent Subacute 4–12 weeks Unresolved infection Chronic > 12 weeks Multifactorial (inflammation, allergy, biofilm, polyp) 2. Common Etiologic Agents Viral

SOP: Resolving Split Hit Patterns in Microbial Identification with Statistical and Biological Confirmation
Goal: make a safe, defensible call (strain vs species) when top hits and lower hits disagree. Inputs you need (from your search output) For BLAST/aligners : E-value, bit score, query coverage (often qcovs), % identity, alignment length For read mapping/WGS : breadth (% of gene covered), depth (× coverage) per marker gene For MALDI-TOF : instrument “score category” (use vendor “high-confidence” tier as species-level; treat “low/borderline” as screening only) Step 0 — Filte

Interpreting Split Hit Patterns in Microbial ID: Clinical Guide to Database-Based Identification
How to interpret mixed database matches and make a safe call Executive summary Don’t trust a single top hit. Look for a cluster of strong, consistent top hits plus biological markers. Use three lenses together: Scores → Coverage → Biology . Practical cut-offs (rules of thumb): E-value floor: keep hits with E ≤ 1e-20 (or stricter for short queries). Separation factor (SF): if the E-value at rank 11 is ≥ 100× the E-value at rank 10, the top-10 cluster is meaningfully st

DEPTh Typing as Diagnosis: Clinical Interpretation of Database-Based Identification
🧭 1. DEPTh Typing: This is a Diagnostic Challenge So your challenge = “Given a biological isolate (bio sample), how do we determine what organism it is — using a database comparison with a score and a hit?” ➡ DEPTh type: Diagnostic The object of study = diagnostic accuracy of a computational or laboratory index test Index test: sequence or spectrum matching algorithm Reference standard: species identification (e.g., culture, gold-standard sequencing) 🔬 2. Diagnostic Lo

To Cut or Not to Cut: Handling Continuous Predictors in Clinical Prediction Models
Abstract Choosing whether to treat predictors as continuous or categorical is one of the most recurrent—and most misapplied—decisions in clinical prediction model (CPM) development. Although categorization improves interpretability, it often sacrifices statistical power, calibration, and discrimination. This article integrates statistical evidence and clinical reasoning to define when, why, and how continuous variables should be modeled or categorized. A structured, evidence-

Diagnosis and Management of Pure Hoarseness (Acute Laryngitis) เสียงแหบ
🧠 Overview Acute laryngitis is the most common cause of hoarseness (dysphonia) .It is usually viral , self-limited, and involves inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa and vocal cords . When hoarseness occurs without other major airway symptoms , it is called “pure hoarseness” — meaning the patient has voice change without dyspnea, stridor, dysphagia, or systemic toxicity . 🧩 Pathophysiology Normally, the vocal cords vibrate symmetrically to produce sound.In laryngitis: Vi

Cohen’s Kappa Explained: Weighted Agreement in Clinical Research
Introduction Why Use Cohen’s Kappa in Diagnostic Research? Cohen’s Kappa (κ) is a widely used statistical measure for assessing agreement between two raters or measurement methods that classify items into categorical outcomes. It adjusts for the agreement that could occur by chance , providing a more realistic and conservative estimate of concordance. Purpose and Applications Measuring Inter-rater or Inter-method Agreement Kappa is primarily used to quantify the level of a

Optimism in Clinical Prediction Models (CPMs) Apparent Performance = Test Performance + Optimism
🔍 Background In the development of Clinical Prediction Models (CPMs) —tools that estimate a patient's risk of future events based on clinical features—researchers often report strong model performance when evaluated using the development dataset. However, these metrics can be misleadingly optimistic. This gap between perceived and true predictive ability is known as optimism . 📊 What Is Optimism? Optimism in CPMs refers to the inflation of performance metrics (e.g., AUROC,

Translating Regression-Type Machine Learning into the Language of Clinical Research
Machine learning isn’t a new species of science — it’s an evolution of the statistical logic that epidemiologists already use. We’ve always modeled the relationship between exposure and outcome, adjusting for confounders and exploring patterns. What ML brings is automation, scalability, and the ability to capture complex, nonlinear, interactive relationships that traditional regression often misses. 1️⃣ Level 1 — Traditional Regression: The Clinical Baseline Before diving int

Scikit-Learn Algorithm Cheat Sheet — Clinical Epidemiology Edition: Choosing the Right ML Type
🟡 START You begin by asking: What kind of problem am I trying to solve in my study? Common scenarios in clinical epidemiology : Identifying patients with a disease → diagnosis Predicting future outcomes → prognosis Estimating biomarkers or lab values → continuous prediction Finding hidden patient subgroups → phenotyping Simplifying many variables into a few patterns → data reduction 🔹 1. Do you have labeled data? YES → Go to Supervised Learning (you know the outcome) e.g.

Hyperthyroidism: Definition, Causes, Diagnosis & Stepwise Management Guide [MMI, PTU]
1️⃣. Definition and Pathophysiology Hyperthyroidism = overproduction of thyroid hormones ( T3, T4 ) by the thyroid gland → suppressed TSH . Thyrotoxicosis = clinical syndrome of excess circulating thyroid hormone, regardless of cause (e.g., Graves, thyroiditis, toxic nodular goiter). Pathophysiology summary: ↑ T3/T4 → ↑ basal metabolic rate ↑ β-adrenergic receptor sensitivity → palpitations, tremor Feedback inhibition → ↓ TSH from pituitary 2️⃣. Common Causes Category Disea

How to Adjust Methimazole (MMI) Dose in Hyperthyroidism: A Step-by-Step Lab-Based Guide
🎯 1. Goal of Therapy Normalize Free T4 (FT4) and Free T3 (FT3) levels. TSH is not reliable early — it remains suppressed for weeks to months even after hormones normalize. The primary lab for dose adjustment = FT4 (± FT3) . 🧪 2. Monitoring Schedule Time after starting MMI Lab to Check Why Baseline TSH, FT4, FT3, CBC, LFT Starting point & safety 4–6 weeks after starting FT4 ± FT3 (ignore TSH) Adjust dose Every 4–6 weeks thereafter FT4 ± FT3 Continue titration Once euthyr

N in Research: More Than a Number — A Measure of Believability, Meaning, and Chance
“N in research represents the p-value — it reflects how believable a result is, or whether the difference is simply due to random change.” In clinical research, we often treat N , the sample size, as a mechanical requirement — something to “get enough patients” or “reach significance.”But that view is incomplete. N is not just a number; it is a claim about credibility. It defines how convincingly we can argue that a difference is real , not random . It connects p-values , cl

Validating a Multi-Step Deduplication Strategy in Systematic Reviews
Introduction Removing duplicate citations is a vital step in systematic reviews. Duplicate records not only inflate the screening workload but also introduce potential bias if counted more than once in the analysis. Effective deduplication ensures that each unique study is represented only once, maintaining both accuracy and efficiency in the review process. One widely validated and reproducible approach is the multi-step deduplication strategy in EndNote, often referred t

From Regression to Neural Networks: A Conceptual Bridge for Clinical Researchers
Abstract Logistic regression and neural networks share a deep mathematical and conceptual structure. Both compute weighted sums of...

Prediction vs Causation in Clinical Research: Using the DEPTh Model to Choose the Right Approach, Causal vs Non‑Causal—How to Choose the Right Study Logic
Clinicians often juggle questions that look similar but actually demand different scientific logics. The DEPTh model (Diagnosis,...

The “10 Events-per-Variable” 10 EPV Rule in Clinical Prediction Modeling
For many years, the 10 Events-per-Variable (EPV) rule was the default checkpoint for building clinical prediction models. The idea is...

The Fontan Procedure and Its Hepatic Complications: Understanding Fontan-Associated Liver Disease (FALD)
1️⃣ What Is the Fontan Procedure? The Fontan procedure is a palliative cardiac surgery performed for children with single-ventricle congenital heart defects , where only one ventricle is capable of supporting systemic circulation. ➤ Purpose: To separate systemic and pulmonary circulation in patients who cannot undergo a biventricular repair. ➤ Indications: Common congenital heart diseases requiring Fontan include: Tricuspid atresia Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) Do

Orchitis Overview: Viral vs Bacterial Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies
🔹 Definition Orchitis is an inflammation of the testicular parenchyma .It can occur as: Primary orchitis (rare, often...

Epididymitis Explained: Diagnosis, Causes, and Treatment by Age and Risk Factors
🔹 Definition Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis , the coiled duct located posterior to the testis responsible for sperm...

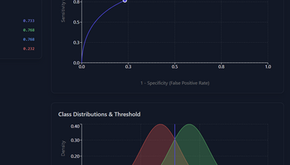
ROC Curve & AUC Explained: Interpretation, Application, and Clinical Relevance
Introduction The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve is a cornerstone metric in both diagnostic and prognostic model...